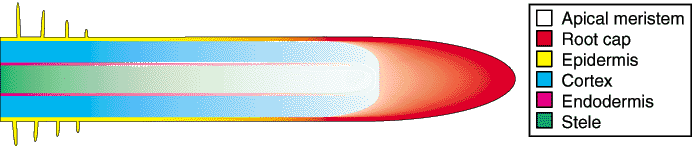
 〔CSIRO(Australia's Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation) Forestry and Forest Productsの中のMycorrhizaの『Section 2. ROOTS』から〕 Apical meristem=頂端分裂組織、Root cap=根冠、Epidermis=表皮、Cortex=皮層、Endodermis=内皮、Stele=中心柱。 |
|
|
|
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
||
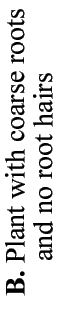
|
 |
 |
|
|
||
|
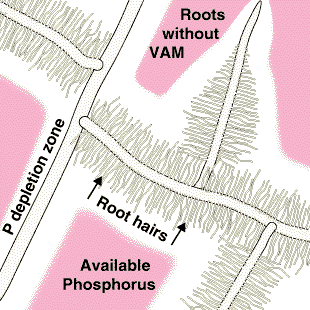
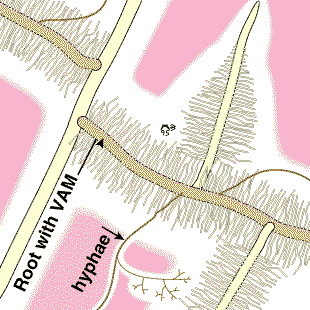
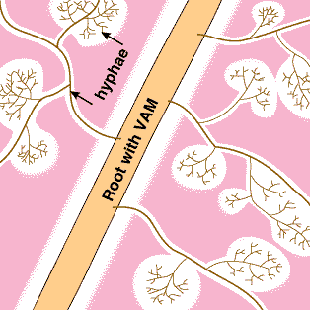
These diagrams have been simplified to assume that phosphorus is uniformly distributed in the soil and is equally available to roots and hyphae. They show the extreme situations of a plant with very fine roots and long hairs (such as many grasses) and a plant with thick roots and no root hairs. There are also many plants with intermediate root systems. これらの図は、リンは土壌中に均一に分布しており、根と菌糸に等しく利用されると仮定して単純化されている。非常に細い根と長い根毛をもつ植物(多くの草)、および太い根で根毛のない植物の、両極端の場合をこれらは示している。これらの中間の根系をもつし植物も多く存在する。 〔CSIRO(Australia's Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation) Forestry and Forest Productsの中のMycorrhizaの『Section 5. ROLES OF MYCORRHIZAS』から〕 |
||
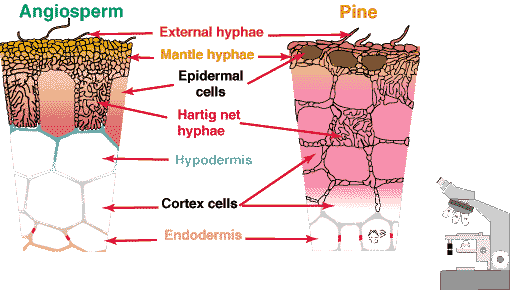 〔CSIRO(Australia's
Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation)
Forestry and Forest Productsの中のMycorrhizaの『Section
4. 外生菌根(ectomycorrhiza)。hypodermis=下皮、cortex=皮層、endodermis=内皮、epidermal cell=表皮細胞、Hartig net=菌糸網(ハルティッヒネット)。 |
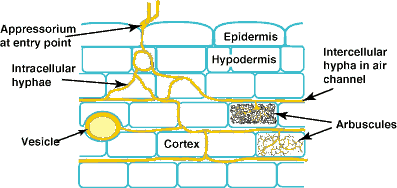 〔CSIRO(Australia's Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation) Forestry and Forest Productsの中のMycorrhizaの『Section 3. ARBUSCULAR MYCORRHIZAS』から〕 内生菌根(endomycorrhiza)。vesicle=嚢状体、arbuscule=樹枝状体、appressorium=付着器。 |
|
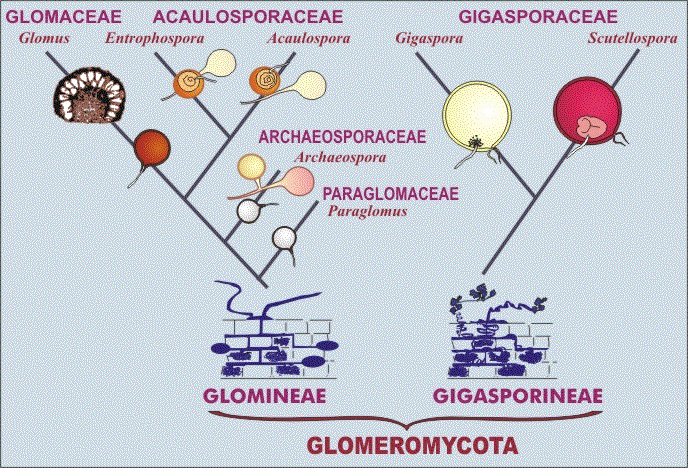
Classification scheme for Glomalean taxa (Morton
& Benny 1990)
〔CSIRO(Australia's Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation) Forestry and Forest Productsの中のMycorrhizaの『Section 3. ARBUSCULAR MYCORRHIZAS』から〕 |
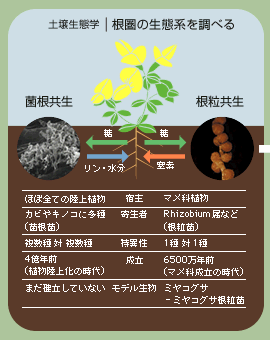 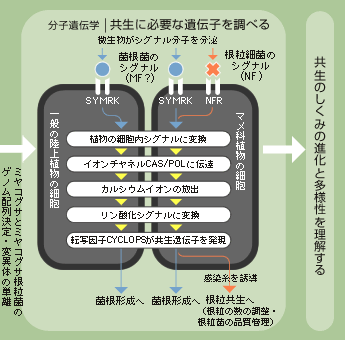 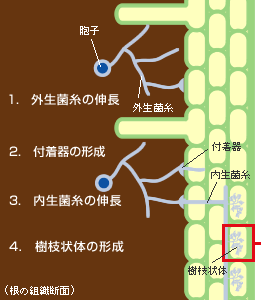 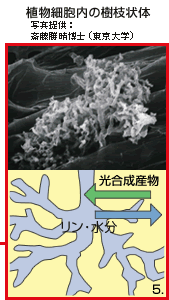 (1.)菌根菌が根を認識すると、(2.)根の表面に付着器を形成し、(3.)そこから内生菌糸を根の内部に伸ばし、(4.)植物の細胞内に樹枝状体とよばれる構造をつくる。(5.) 菌根菌は土壌から集めたリンや水分などを植物に提供する一方、植物の光合成産物を自身のエネルギー源に利用する。 〔大阪大学大学院 工学研究科 林誠氏による『共生のしくみ−植物と土壌微生物の遺伝子ネットワーク』から〕 |