Sauer,D., Saccone,L., Conley,D.J., Herrmann,L.
and Sommer,M.(2006): Review of methodologies for extracting
plant-available and amorphous Si from soils and aquatic sediments.
Biogeochemistry, 80, 89-108.
『土壌と水中堆積物から植物が利用できて非晶質のケイ素を抽出するための方法論のレビュー』
『Abstract
There is a variety of methodologies used in the aquatic sciences
and soil sciences for extracting different forms of Si from sediments
and soils. However, a comparison of the published extraction techniques
is lacking. Here we review the methodologies used to extract different
Si fractions from soils and sediments. Methods were classified
in those to assess plant-available Si and those to extract Si
from amorphous silica and allophane. Plant-available Si is supposed
to comprise silicic acid in soil solution and adsorbed to soil
particles. Extraction techniques for plant-available Si include
extractions with water, CaCl2, acetate, acetic
acid, phosphate, H2SO3,
H2SO4, and citrate.
The extractions show different capabilities to desorb silicic
acid, with H2SO3, H2SO4 and citrate having the
greater extraction potential. The most common extractions to dissolve
amorphous silica from soils and aquatic sediments are NaOH and
Na2CO3, but both also
dissolve crystalline silicates to varying degrees. In soils moreover
Tiron is used to dissolve amorphous silica, while oxalate is used
to dissolve allophanes and imogolite-type materials. Most techniques
analyzing for biogenic silica in aquatic environments use a correction
method to identify mineral derived Si. By contrast, in the soil
sciences no correction methods are used although pedologists are
well aware of the overestimation of amorphous silica by the NaOH
extraction, which is most commonly used to extract silica from
soils. It is recommended that soil scientists begin to use the
techniques developed in the aquatic sciences, since it seems impossible
to extract amorphous Si from soils completely without dissolving
some of the crystalline silicates.
Key words: Adsorbed silica; Alkaline extraction methods; Amorphous
silica; Biogenic silica; Dissolved silica; Silicic acid』
Introduction
Methods for extracting plant-available Si
H2O and CaCl2
Acetate and acetic acid
Phosphate-acetic acid and phosphate buffer solution
Citrate and citric acid
Sulfur acid (H2SO4)
and sulfurous acid (H2SO3)
Studies comparing different methods to extract plant-available
Si from soils
Methods for extracting Si from amorphous silica, allophane, and
imogolite-type materials
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
NaOH extractions applied to soils
NaOH extractions applied to aquatic systems and to sediments
Sodium carbonate (Na2CO3)
Na2CO3 extractions
applied to soils
Na2CO3 extractions
applied to aquatic systems and sediments
Studies comparing the NaOH and Na2CO3 extraction
Tiron
Oxalate
Summary and conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
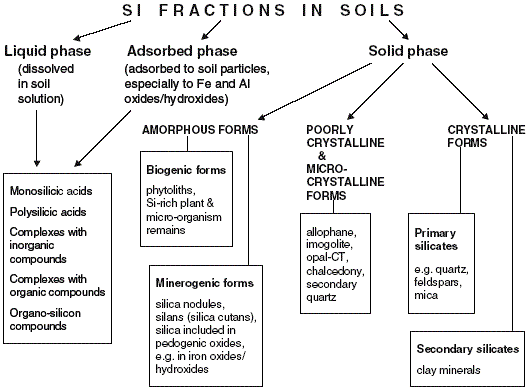
Figure 1. Classification of silicon compounds in the soil
(modified from Matichencov and Bocharnikova 2001).
〔Sauer,D., Saccone,L., Conley,D.J., Herrmann,L. and Sommer,M.(2006):
Review of methodologies for extracting plant-available and
amorphous Si from soils and aquatic sediments. Biogeochemistry,
80, 89-108.による〕 |
- Matichencov,V.V. and Bocharnikova,E.A.(2001): The relationship
between silicon and soil physical and chemical properties.
In: Datnoff,L.E., Snyder,G.H. and Korndorfer(後のoの頭に¨),G.H.(eds.),
Silicon in Agriculture. Elsevier Science B.V., 209-219.
戻る
