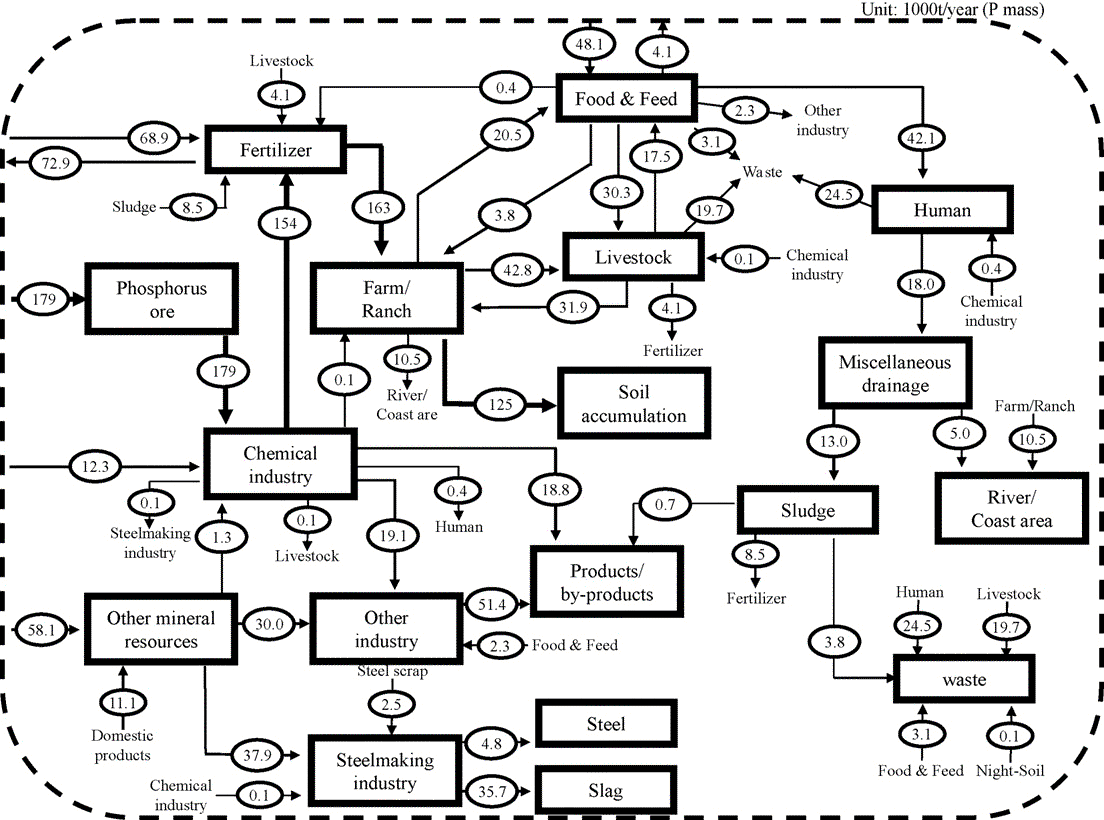
 Fig. 3. Domestic
material flow of phosphorus in South Korea (2005).
Fig. 3. Domestic
material flow of phosphorus in South Korea (2005).〔Jeong,Y.-S., Matsubae-Yokoyama,K., Kubo,H., Pak,J.-J. and Nagasaka,T.(2009)によるSubstance flow analysis of phosphorus and manganese correlated with South Korean steel industryから〕
『Abstract
Security of resources becomes more important than ever as the
upward trend in the prices of mineral and natural resources continues.
Phosphorus and manganese are important minerals to many countries.
Phosphorus is in global demand, particularly for making fertilizers,
and manganese is an indispensable element in industrial and consumer
products. However, the raw materials for these two elements are
restricted to certain geographical regions and countries. More
importantly, they are not produced in South Korea, although domestic
use of each is increasing. In this paper the authors examine domestic
phosphorus and manganese flows in South Korea, focusing on the
iron and steel industries and using statistical data for 2005.
The total phosphorus and manganese usage in South Korea are evaluated
to be 380 kt-P/year and 303 kt-Mn/year (manganese ore + manganese
alloy). further, the amounts of phosphorus and manganese lost
to steelmaking slag are estimated to be 35.7 kt-P/year and 162
kt-Mn/year. These losses correspond to about 10% of the domestic
phosphorus consumption and approximately 53% of the manganese
added in steelmaking processes as an alloying element or deoxidation
agent. The results from these substance flow analyses suggest
that a significantly large ripple effect can be expected if recovery
of phosphorus and manganese from slag becomes possible. The potential
for concerting steelmaking slags into new phosphorus and manganese
resources is also discussed from the viewpoint of recovery technology.
Keywords: Material flow analysis; Phosphorus; Resource management;
Manganese; Steelmaking slag』
Contents
1. Introduction
2. Phosphorus material flow in South Korea
2.1. Primary sector: agriculture, livestock, and fishery
sector
2.2. Industrial sector
2.3. Environmental sector
2.4. Domestic flow of phosphorus in South Korea
3. Manganese material flow in South Korea
4. Phosphorus and manganese recovery from slag
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgment
References
 Fig. 3. Domestic
material flow of phosphorus in South Korea (2005). Fig. 3. Domestic
material flow of phosphorus in South Korea (2005).〔Jeong,Y.-S., Matsubae-Yokoyama,K., Kubo,H., Pak,J.-J. and Nagasaka,T.(2009)によるSubstance flow analysis of phosphorus and manganese correlated with South Korean steel industryから〕 |
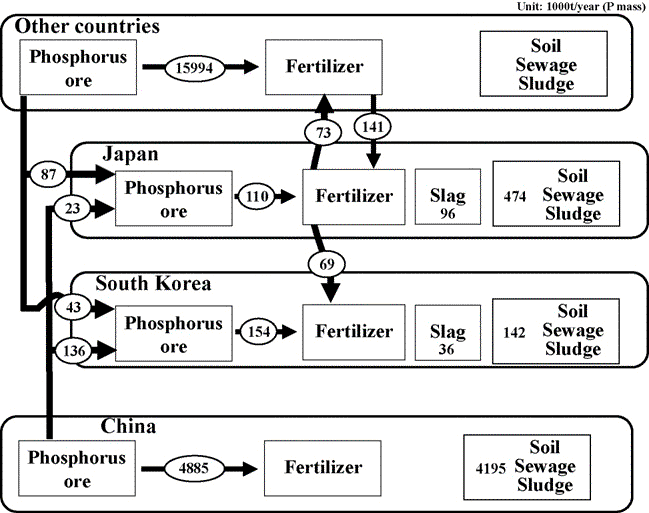 Fig. 7. Phosphorus flow among South Korea, Japan, China and other phosphate ore exporting countries. 〔Jeong,Y.-S., Matsubae-Yokoyama,K., Kubo,H., Pak,J.-J. and Nagasaka,T.(2009)によるSubstance flow analysis of phosphorus and manganese correlated with South Korean steel industryから〕 |