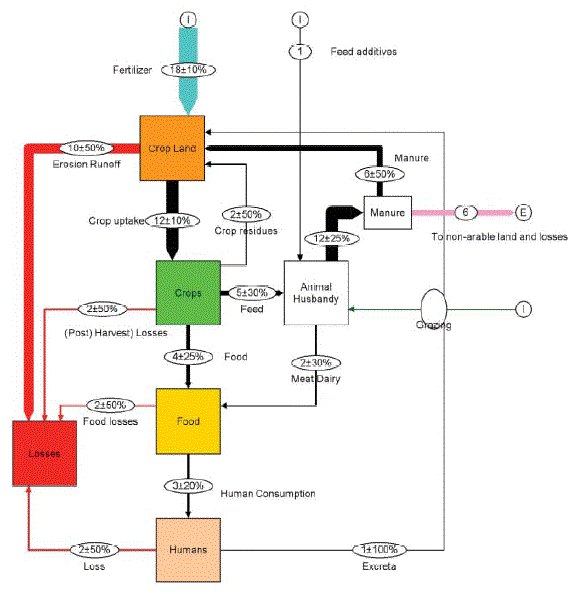
Smit,A.L., Bindraban,P.S., Schroder(oの頭に´), J.J., Conijn,J.G. and vander Merr,H.G.(2009)による『Phosphorus in agriculture: global resources, trends and developments』から
図1.入力(I、流入)と出力(O、流出)および耕地の食料生産体系(Cordell, 2008, 2009による)を通じてSmil(2000, 2007)とLiu et al.(2008)のデータと我々の計算も考慮した、世界における主要なリン・フロー図