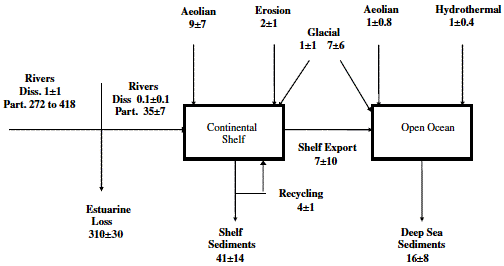
Fig. 5. The global iron (oxyhydr)oxide cycle. Units in Tg yr-1.
kRaiswell,R., Tranter,M., Benning,L.G., Siegert,M., De'ath,R., Huybrechts,P. and Payne,T.(2006): Contributions from glacially derived sediment to the global iron (oxyhydr)oxide cycle: Implications for iron delivery to the oceans. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70, 2765-2780.©ηl