Chen,W. and Xu,R.(2010): Clean coal
technology development in China. Energy Policy, 38,
2123-2130.
『中国のクリーンコールテクノロジーの発達』
『Abstract
Coal is found in huge amounts throughout the world and is expected
to play a crucial role as an abundant energy source. However,
one critical issue in promoting coal utilization is controlling
environmental pollution. Clean coal technologies are needed to
utilize coal in an environmentally acceptable way and to improve
coal utilization efficiency. This paper describes coal's role
in China's energy system and the environmental issues related
to coal use. Coal is responsible for 90% of the SO2
emissions, 70% of the dust emissions, 67% of the NOx emissions,
and 70% of the CO2 emissions. But as the
most abundant energy resource, it will continue to be the dominant
energy supply for a long time. Therefore, the development and
deployment of clean coal technologies are crucial to promote sustainable
development in China. Clean coal technologies currently being
developed in China are described including high efficiency combustion
and advanced power generation technologies, coal transformation
technologies, IGCC (integrated gasification combined cycle) and
carbon capture and storage (CCS). Although China only recently
began developing clean coal technologies, there have been many
successes. Most recent orders of coal-fired power plants are units
larger than 600 MW and new orders for supercritical and ultra
supercritical systems are increasing rapidly. Many national research
programs, industrial research programs and international collaboration
projects have been launched to develop on IGCC and CCS systems
in China. Finally, suggestions are given on how to further promote
clean coal technologies in China.
Keywords: China; Clean coal technology; Sustainable development』
1. China's coal dominant energy system
1.1. Coal: the most abundant fossil energy resource
1.2. Coal provides around 70% of the total primary energy consumption
1.3. Power sector consumed nearly half of the coal
1.4. Coal consumption in end-use demand sectors
2. Coal: the major source of local air pollution and carbon emissions
2.1. Local air pollution
2.2. Carbon emissions
3. Current status and development of clean coal technologies in
China
3.1. High efficiency combustion and advanced power generation
technologies
3.1.1. Supercritical and ultra-supercritical systems
3.1.2. Circulating fluidized beds
3.1.3. Flue gas desulphurization and NOx removal
3.2. Coal transformation
3.2.1. Gasification
3.2.2. Liquefaction
3.3. Integrated gasification combined cycle (IGCC)
3.4. Carbon capture and storage technology
3.4.1. National science and technology programs for CCS in China
3.4.2. China's industrial development of CCS
3.4.3. International partnerships on CCS
4. Concluding remarks
References
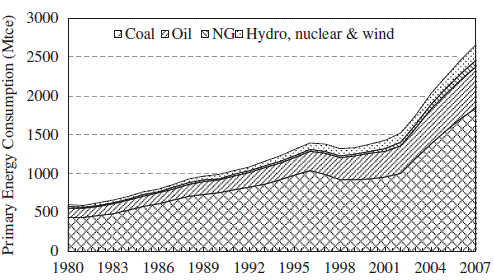
Fig. 2. China’s primary energy consumption from 1980 to
2007.
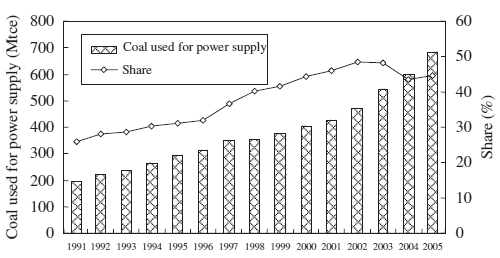
Fig. 3. Coal consumption for power and the % of coal used
for power in the total coal consumption.
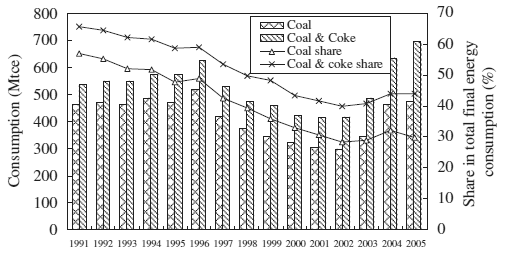
Fig. 5. Coal Consumption and Percentage in the total final
energy consumption from 1991to2005. |
ホームへ


