Hammond,G.P.(2006): ‘People, planet
and prosperity’: The determinants of humanity's environmental
footprint. Natural Resources Forum, 30, 27-36.
『「人々、惑星そして繁栄」:人間の環境フットプリントの決定要素』
『Abstract
Environmental or ‘ecological’ footprints have been widely used
in recent years as indicators of resource consumption and waste
absorption on the basis of biologically productive land area required
per capita with prevailing technology. Such footprints represent
a partial measure of the extent to which the planet, its regions,
or nations are moving along a sustainable development pathway.
They vary between countries at different stages of economic development
and varying geographic characteristics. The determinants of environmental
footprints in some 113b countries from around the world have been
evaluated. Dimensional analysis techniques from engineering and
the physical sciences are employed to determine the relative significance
of population density, economic wealth, and intensity of pollutant
emission. Variations about the resulting ‘power-law’ correlation
suggest the extent to which individual nations are currently frugal
or profligate in terms of their resource use and environmental
impacts. The scatter associated with footprints, or closely related
parameters, also indicates the uncertainty inherent within the
international datasets needed to compute them, as well as differences
in local climate and terrain. Nevertheless, national footprints
alert humanity to the necessity of living within the regenerative
capacity of the biosphere in order to ensure ‘environmental sustainability’.
Keywords: Environmental footprints; Resource use; Carbon emissions;
International development; Sustainability』
1. Introduction
2. The sustainable development context
3. Methods
3.1. Environmental footprint analysis: The background
3.2. Environmental footprints of nation States
4. Results and discussion
4.1. The determinants of national environmental footprints
4.2. Overshooting national carrying capacity
4.3. Some implications for international negotiations on greenhouse
gas emissions
5. Concluding remarks
Acknowledgements
References
- National environmental footprints (ef) = function {population
density (PD), economic wealth (GNI), energy intensity (EI), and
carbon emissions ratio (CR)}
- ef = constant {PDm GNIn EIp
CRq}
- Population size in millions and land area in km2
from the WWF (Loh, 2002)
- Per capita GNI in international dollars from the World
Bank's World Development Report 2002
- Primary energy use in EJ from BP Statistical Review of
World Energy 2004
- CO2 emissions in Mt, also from the World
Bank (2002)
- ef = 0.00658 PD-1/4 GNI2/3
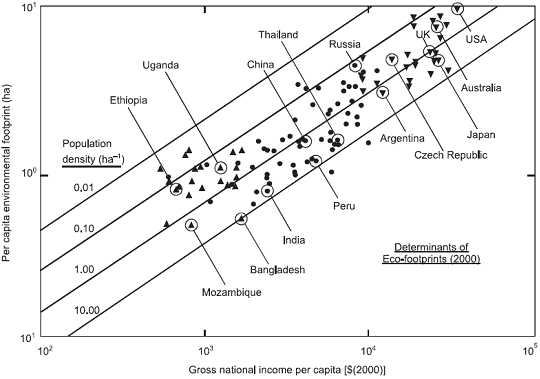
Figure 4. The determinants of humanity's environmental
footprint. Solid line: correlation equation for prescribed
population densities. World Bank
categorisation of States: high income ▼; medium income ●; low
income ▲ (The World Bank, 2002). Selected countries identified.
〔Hammond,G.P.(2006): ‘People, planet and prosperity’: The
determinants of humanity's environmental footprint. Natural
Resources Forum, 30, 27-36.から〕 |
- British Petroleum(2004): BP
Statistical Review of World Energy. BP plc, London,
June 2004..
- Loh,J.(Ed.)(2002): Living
Planet Report 2002. WWF International, Gland, Switzerland.
- Loh,J.(Ed.)(2004): Living
Planet Report 2004. WWF International, Gland, Switzerland.
- Jorgensen(oには/を付ける),A.E., Vigsoe(oには/を付ける),D., Kristoffersen,A. and Rubin,O.(2002):
Assessing
the Ecological Footprint: A Look at the WWF's Living Planet Report
2002. Danish Environmental Assessment Institute,
Copenhagen.
- World Bank(2002): World
Development Report 2002: Building Institutions for Markets.
Oxford University Press, Oxford.
戻る
