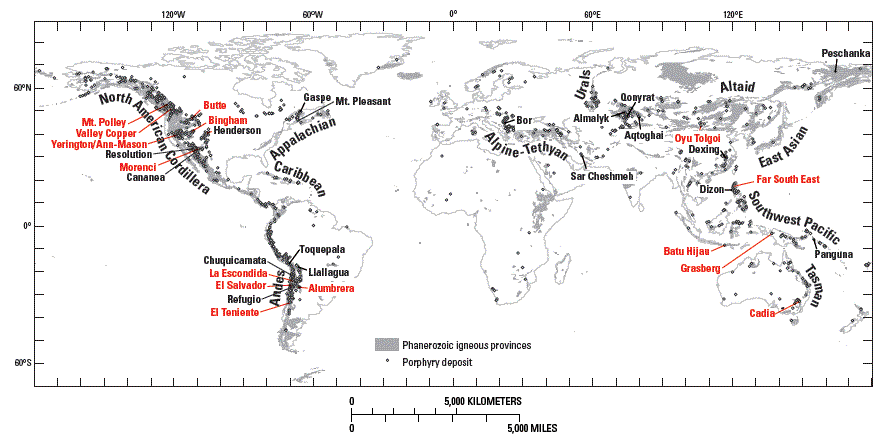
Figure A1. Phanerozoic porphyry belts, porphyry deposits, and representative porphyry copper deposits summarized in Appendix 2 (red labels). Modified from Seedorff and others (2005, their Fig. 1).
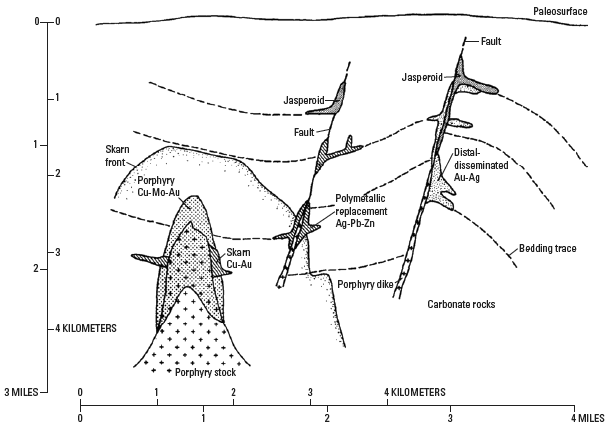
Figure B1. General setting of porphyry copper and associated deposit types (modified from Sillitoe and Bonham, 1990).
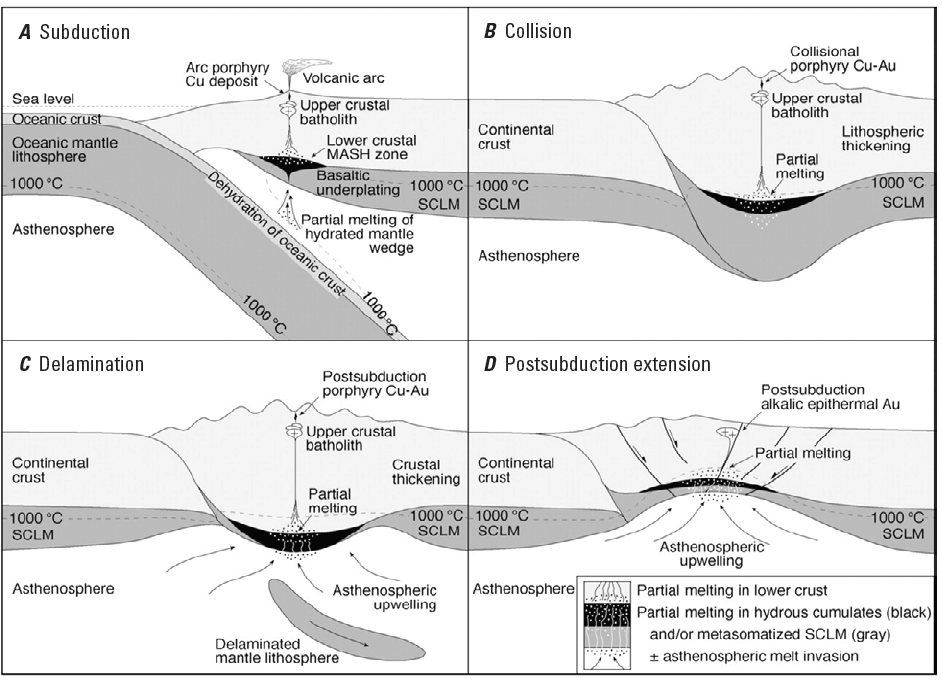
Figure D1. Plate tectonic setting of porphyry copper deposits.
(A) Typical continental margin arc above subduction zone. Porphyry
copper generation as a product of normal arc magmatism; continental
arc is shown, but similar processes can occur in mature island
arcs. MASH.melting, assimilation, storage, and homogenization.
SCLM.subcontinental lithospheric mantle.
(B-D) Remelting of subduction-metasomatized SCLM or lower crustal
hydrous cumulate zones (black layer) leading to potential porphyry
copper-gold and epithermal gold deposit formation.
(B) Collisional lithospheric thickening.
(C) Postcollisional lithospheric mantle delamination.
(D) Postsubduction lithospheric extension. High strontium/yttrium
and lanthanum/ytterbium magmas may be generated in all cases
by residual or fractionating hornblende (±garnet, titanite) in
the lower crust. Reproduced from Richards (2009, his Fig. 1).
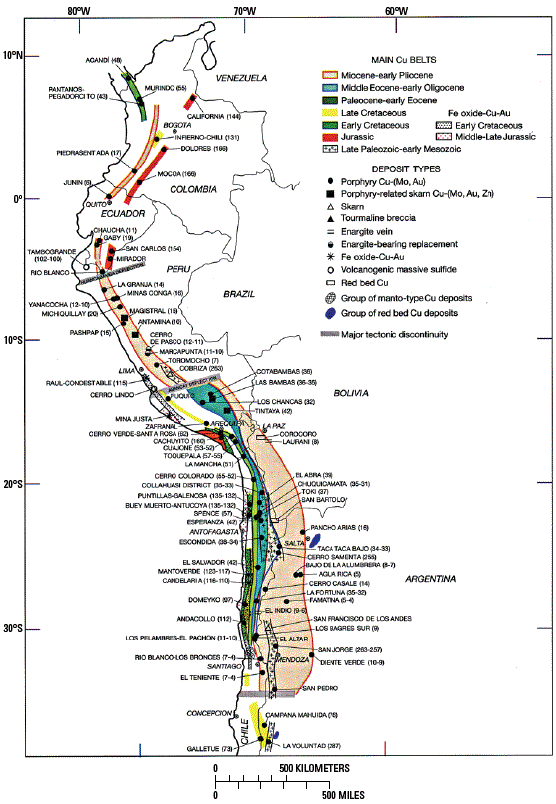
Figure D2. Porphyry copper belts and major porphyry copper deposits in the Andes. From Sillitoe and Perello (2005, their Fig. 2).
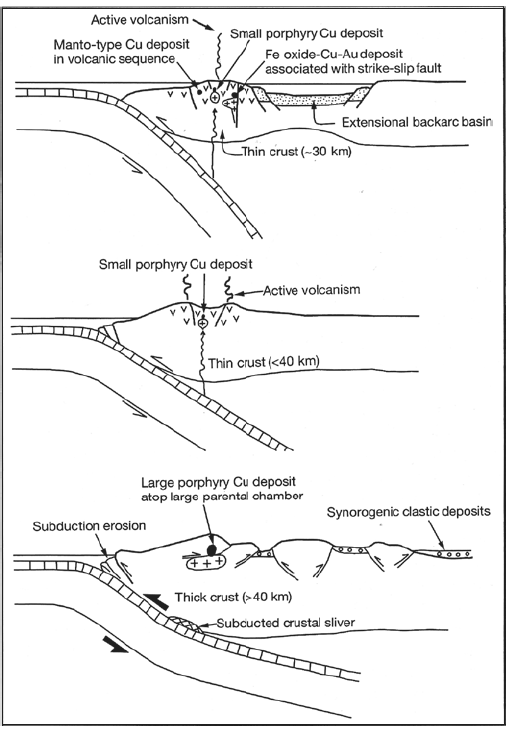
Figure D3. Optimum conditions for development of giant porphyry copper deposits. From Sillitoe and Perello (2005, their Fig.15).
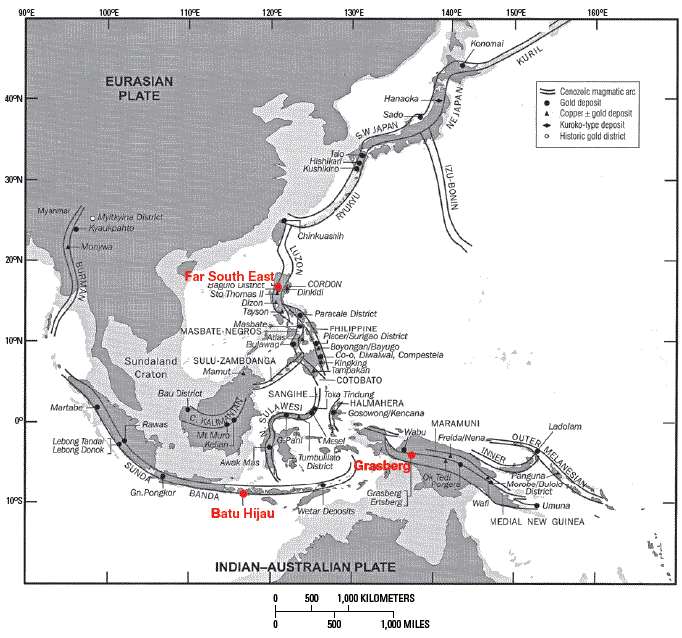
Figure D4. Southeast Asia and the west Pacific showing major Cenozoic arcs and copper ± gold and gold deposits. Porphyry copper deposits summarized in Appendix 2 are shown in red. From Garwin and others (2005, their Fig. 2).
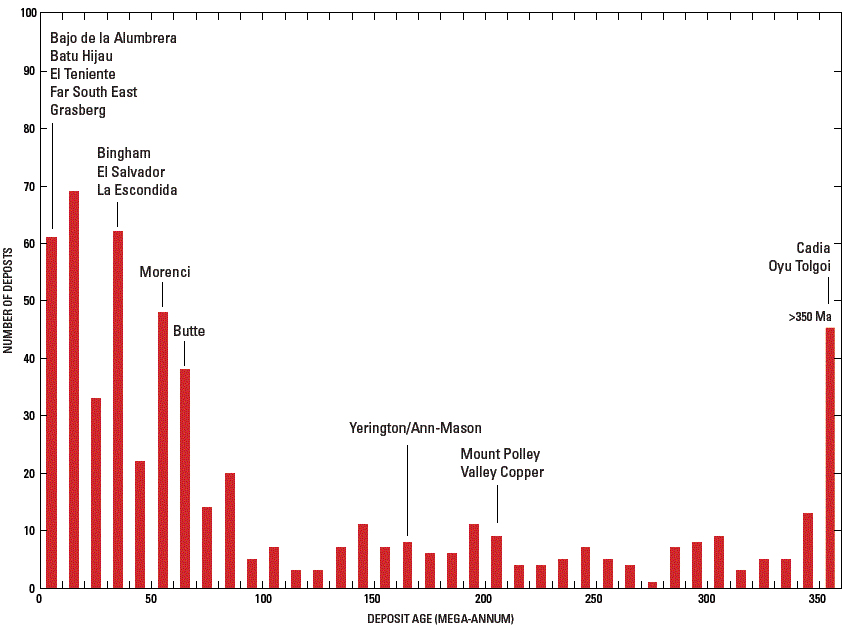
Figure D5. Ages of known porphyry copper deposits. Labeled deposits summarized in Appendix 2. Age data from Singer and others (2008).
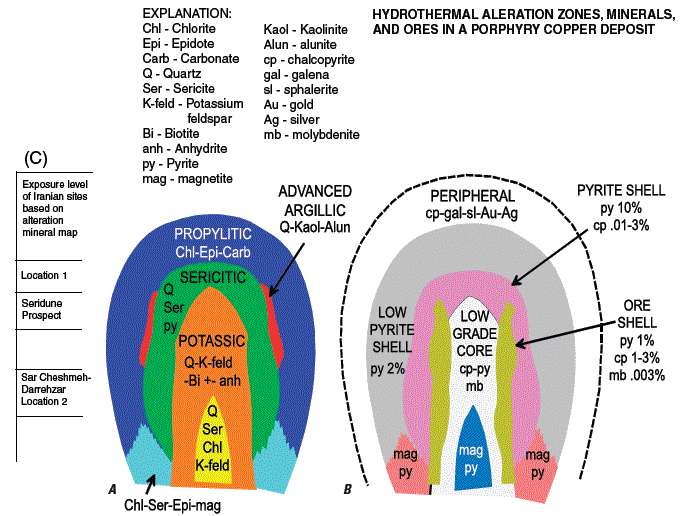
Figure F5. Illustrated deposit model of a porphyry copper
deposit (modified from Lowell and Guilbert, 1970).
(A) Schematic cross section of hydrothermal alteration minerals
and types, which include propylitic, sericitic, advanced argillic,
and potassic alteration.
(B) Schematic cross section of ores associated with each alteration
type.
(C) Scale showing level of interpreted exposure for Iranian alteration
sites based on ASTER mapped alteration units.
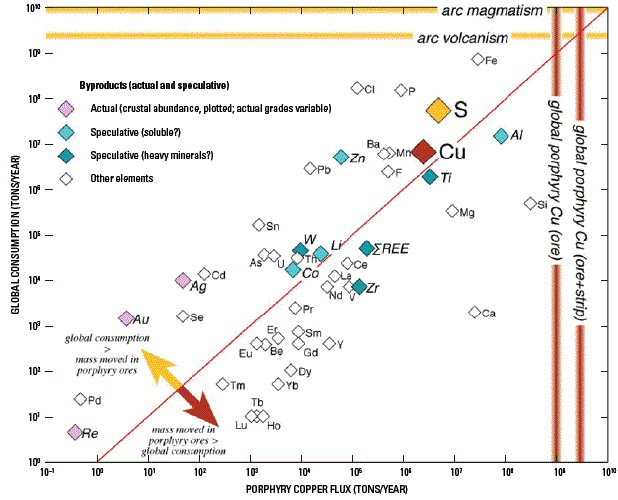
Figure U1. Estimates of the annual flux of elements (diamond symbols) mined (in tons/year ore and waste) during the production of porphyry deposits (porphyry copper flux) as compared to annual global consumption of the same elements (tons/year). Elements that plot above the diagonal line have annual consumption greater than the masses of these elements contained in rock mined in porphyry copper deposits (for example, Cu, S, Au, Ag, Re), whereas elements below this line have masses in rock moved in porphyry copper deposits greater than their annual consumption (for example, Al, Ti, Zr, total REE). Note that many elements in porphyry copper deposits are in gangue or waste rock and are not recovered during ore processing. Also shown are estimates (thick colored orthogonal lines) for the masses of ore and total rock moved (ore + strip) during annual mining of porphyry copper deposits and for the annual masses of arc volcanism and total arc magmatism (volcanism and plutonism). The total mass of rock moved annually by global porphyry copper deposit mining is approximately equal to the annual mass of arc volcanism.
John,D.A.(ed.)(2010)による『Porphyry Copper Deposit Model』から