OECD/IEA(2010): Technology
Roadmap Solar photovoltaic energy. 48p.
『太陽発電エネルギー技術ロードマップ』
Table of Contents
Key findings 3
Introduction 5
The rationale for PV 5
The purpose of the roadmap 6
PV status today 7
Technology performance and cost 7
Market trends 9
Research and development 11
Vision for PV deployment and CO2 abatement
potential 13
Electricity generation and cumulative installed capacity 13
Applications and market end-use sectors 17
Cost reduction goals 18
PV market deployment and competitiveness levels 19
CO2 emissions reduction 21
Technology development: Strategic goals and milestones
22
Technology trends 22
Specific technology goals and R&D issues 23
Policy frameworks: Roadmap actions and milestones 27
Regulatory framework and support incentives 27
Market facilitation and transformation 29
Technology development and RD&D 30
International collaboration 32
Conclusion: Actions for stakeholders
and next steps 35
Appendix I. References and roadmaps consulted 37
Appendix II. List of relevant websites 39
Appendix III. List of workshop participants and reviewers 40
Appendix IV. Abbreviations, acronyms and units 42
Conclusion: Actions
for stakeholders and next steps
This roadmap has responded to the G8 and other government leaders’
requests for more detailed analysis regarding the growth pathway
for PV
energy, an important GHG mitigation technology. It describes approaches
and specific tasks regarding PV research, development, and deployment;
financing mechanisms; grid integration; legal and regulatory frameworks;
public engagement; and international collaboration. It provides
regional
and end-use sector projections for PV deployment from 2010 to
2050. The roadmap identifies the next decade as a critical time
window in order to accelerate the development and deployment of
PV technologies. Achieving this roadmap’s vision will require
a strong, long-term and balanced policy effort in the next decade
to allow for optimal technology progress, cost reduction and ramp-up
of industrial manufacturing for mass deployment. Priority actions
for the next ten years include:
- Provide long-term targets and supporting policies to build
the needed confidence for investments in manufacturing capacity
and
deployment of PV systems. Implement effective and cost-efficient
PV incentive schemes, which will have to be transitional and
decrease over time, in order to foster innovation and technological
improvement.
- Develop and implement appropriate financing schemes, in particular
for rural electrification and other applications in developing
countries.
- Increase R&D efforts to reduce costs and ensure PV readiness
for rapid deployment, while also supporting longer-term innovations.
The table below details actions and milestones to aid policy
makers, industry and power-system actors in their efforts to successfully
implement PV energy.
The PV roadmap is meant to be a process, one that evolves to take
into account new technology developments, policies and international
collaborative efforts. The roadmap has been designed with milestones
that the international community can use to ensure that PV energy
development efforts are on track to achieve the GHG emissions
reductions that are required by 2050. As such, the IEA, together
with government, industry and NGO stakeholders will report regularly
on the progress that has been achieved toward this roadmap’s vision.
For more information about the PV roadmap inputs and implementation,
including additional analysis that informed the conclusions in
this document, visit www.iea.org/roadmaps.
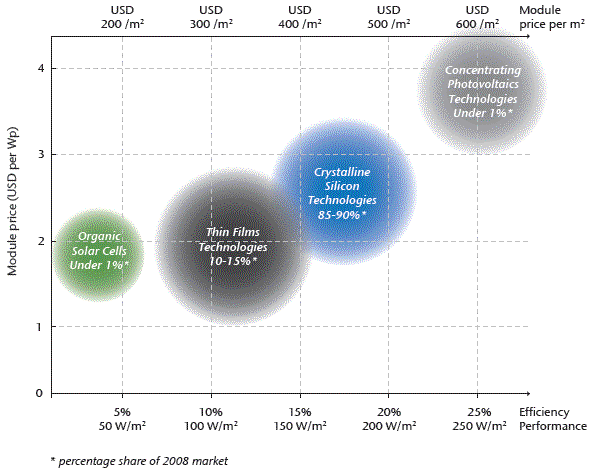
Figure 1: Current performance and price of different PV module
technologies*
Note: all values refer to 2008
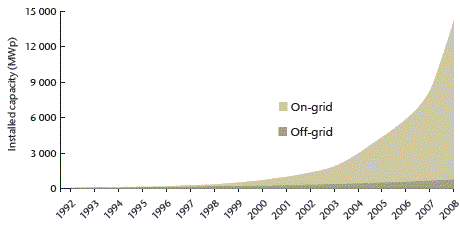
Figure 2: Cumulative installed global PV capacity
Source: IEA PVPS for those IEA PVPS countries reporting data;
estimates for other countries.
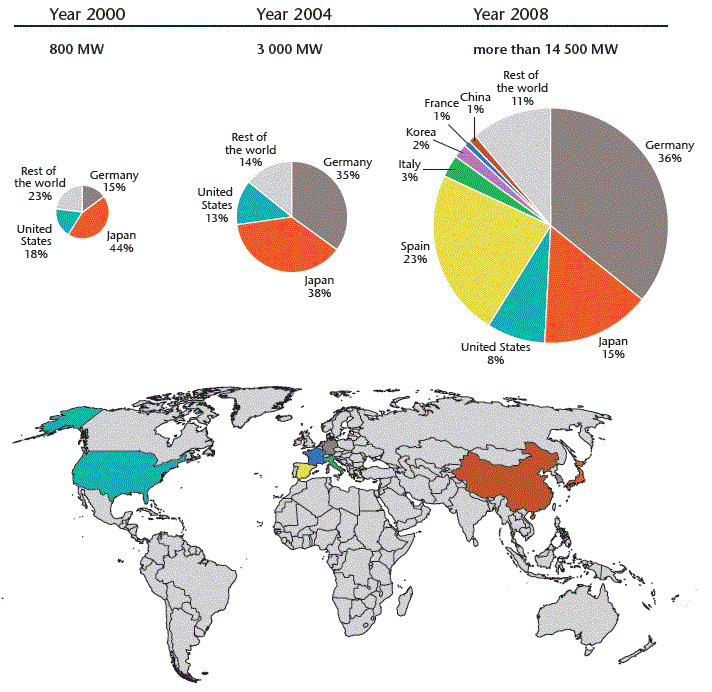
Figure 3: Solar PV markets in leading countries
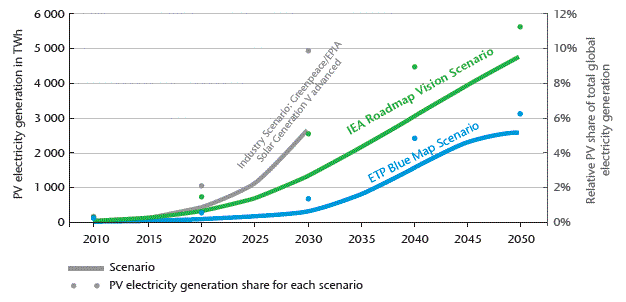
Figure 5: Global PV power generation and relative share of
total electricity generation
Note: The share of total electricity generation is calculated
with the projected world lectricity.
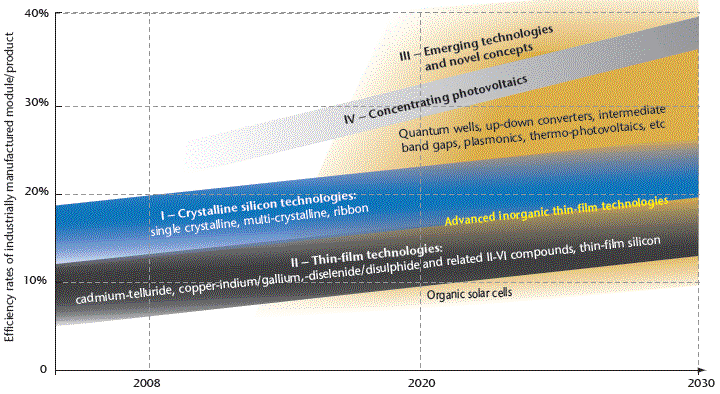
Figure 11: Photovoltaic technology status and prospects
Source: IEA PVPS.
OECD/IEA(2010)による『Technology
Roadmap Solar photovoltaic energy』から |
ホームへ




