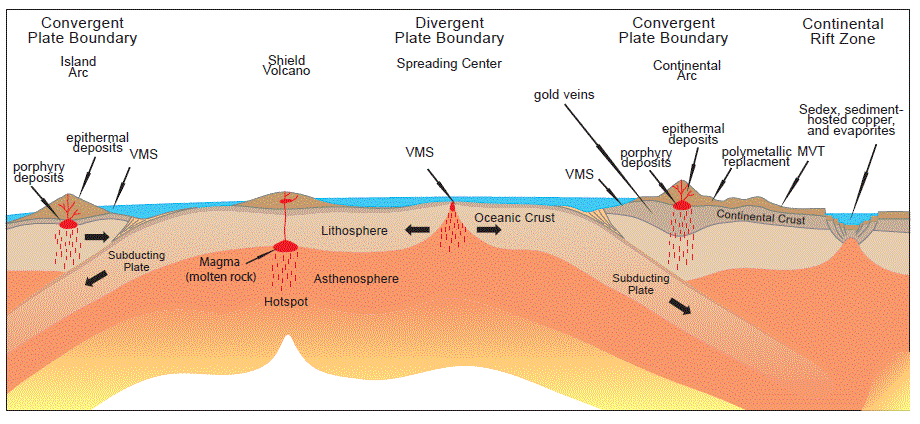
Figure 5 Diagram illustrating the plate tectonic setting in
hich several ma or types of mineral deposits are formed The diagram
sho s
a divergent plate boundary (spreading center) where tectonic
plates are moving apart from each other and lava flows are extruded
on
the ocean floor forming a line of undersea mountains that encircle
the Earth. Iceland, in the north Atlantic, is the tip of one
part of this
mountain range. Volcanogenic massive sulfide (VMS) deposits (described
in the text) are an example of mineral deposits that form on
the sea floor. Also shown are convergent plate boundaries where
an oceanic plate is being subducted beneath a continental tectonic
plate forming folded and faulted mountains (orogen) and volcanoes.
The subduction of oceanic tectonic plates is accompanied by strong
earthquakes and the generation and movement of tmagma (molten
rock) and hydrothermal fluids that form a variety of mineral
deposits,
including porphyry copper deposits and associated gold and silver
veins and polymetallic replacement deposits and associated gold
and silver veins and polymetallic replacement deposits described
in this report. Continental rift zones are areas where the crust
is
stretched (extended) forming linear depressions characterized
by faults, volcanoes, sedimentary basins, and a variety of mineral
deposit
types including sediment-hosted (sedex) lead-sinc, sediment-hosted
copper, and evaporite deposits. See text for further discussion.
Modified from Kious and Tilling (1996).
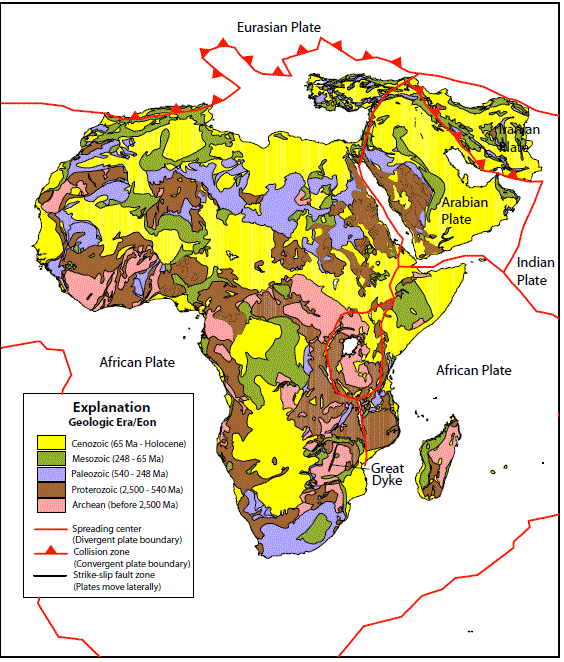
Figure 6. Geologic map of Africa and the Middle East showing the ages of principal rock units and the location of tectonic plate and plate b oundaries. Modified from Kirkham and others (1995).
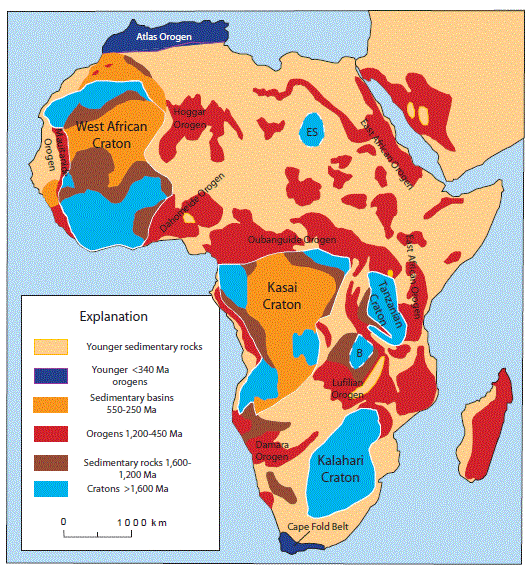
Figure 7A. Map showing selected geologic and tectonic features of Africa. The small cratonic nuclei of the Bangweulu craton is depicted with a "B" and the East Saharan craton with "ES". Modified from Dallmeyer and Lecorche (1991).
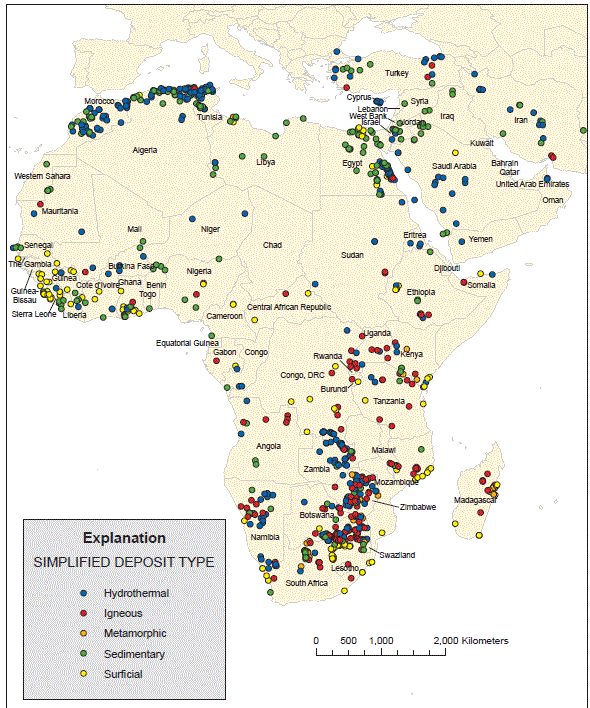
Figure 9A. Map showing distribution of principal nonfuel mineral deposits in Africa and the Middle East by simplified deposit type. There is a tendency for surficial laterite deposites to form in tropical settings near the equator; surficial placer deposits form in fluvial, lacustrine, and coastal marine environment. Hydrothermal deposits tend to form in mountain ranges and in basins affected by orogenic activity and igneous deposits to be localized in island arcs, continental margin arces, and to a lesser extent in stable shields.
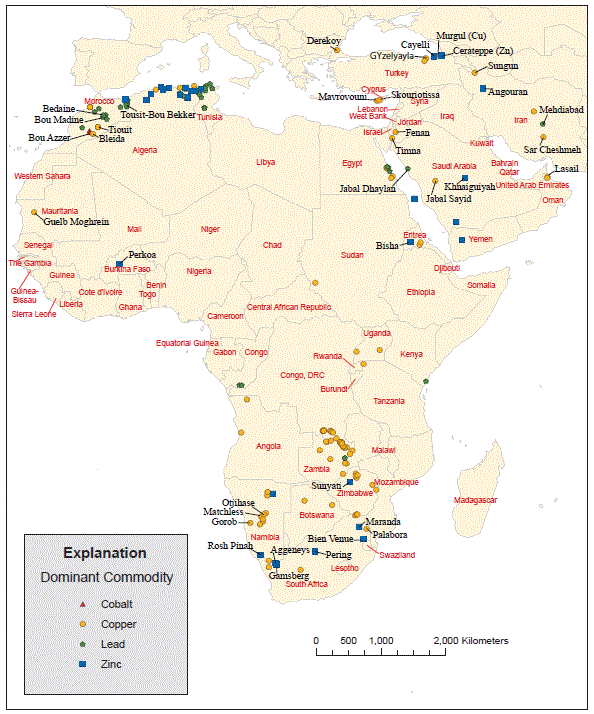
Figure 9B. Map showing location of major deposits of zinc, lead, cobalt, and copper.
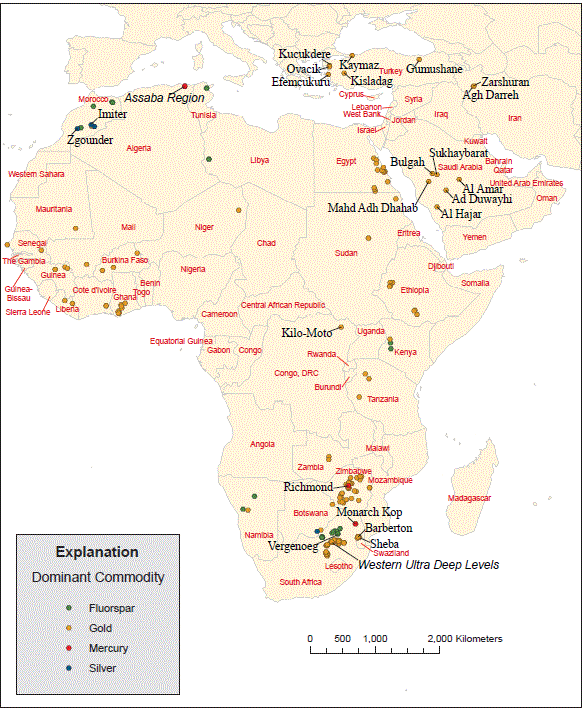
Figure 9C. Map showing location of major deposits of silver, gold, mercury, and fluorspar (fluorite).
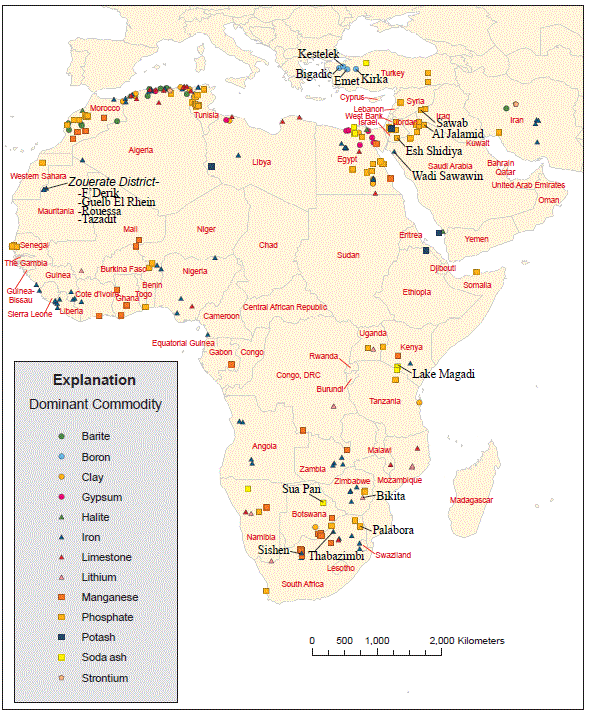
Figure 9D. Map showing location of major deposits of strontium, sodium carbonate, potash, phosphate, managanese, lithium, limestone, clay (bentonite and kaolin), iron, halite (salt), gypsum, boron, and barite.
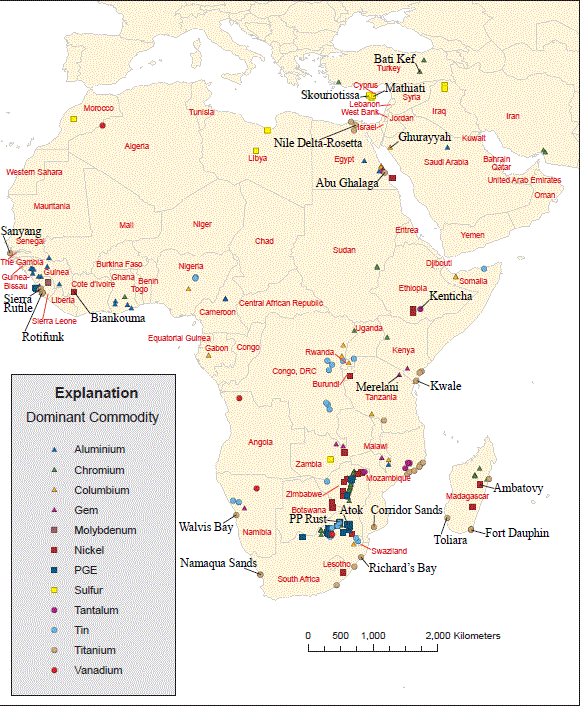
Figure 9E. Map showing location of major deposits of titanium, tin, tantalum, vanadium, sulfur, chromium, platinumgroup elements (PGE), nickel, molybdenum, gemstones, columbium, and aluminum.
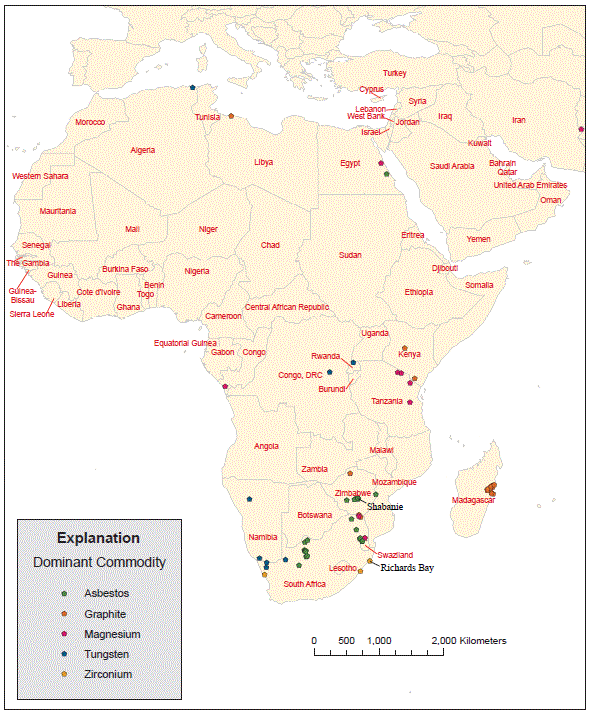
Figure 9F. Map showing location of major deposits of tungsten, magnesium, graphite, zirconium, and asbestos.
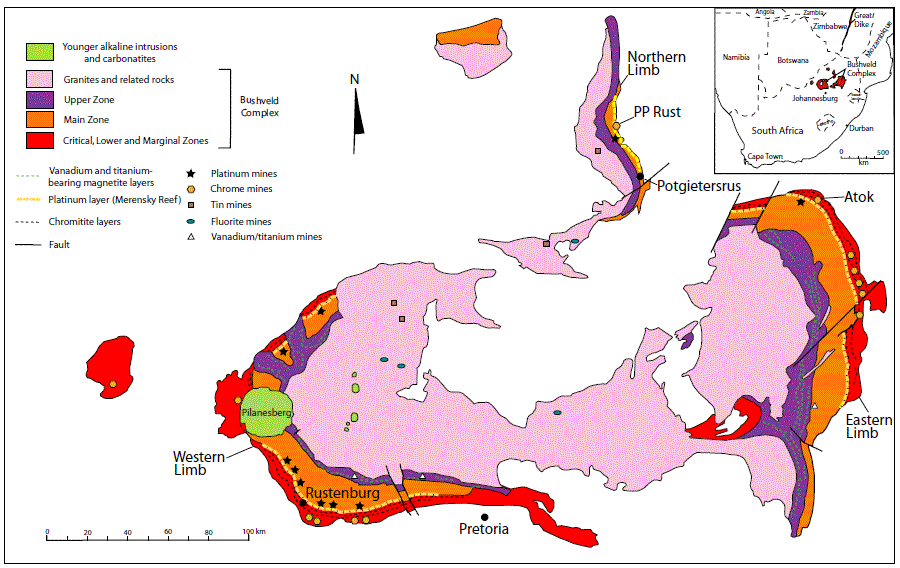
Figure 10H. Simplified geologic map of the Bushveld Igneous Complex, showing locations of some of the more important chromium and PGM mines. Modified from Viljoen and Schurmann (1998).
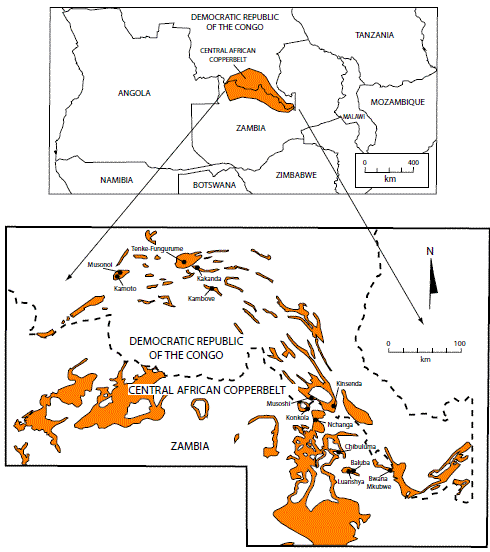
Figure 10I. Simplified geologic map of the Central African Copperbelt showing the distribution of the Katanga Supergroup and some of the regions major mines. Modified from Francois, (1974) and Cailteux and others, (2005).
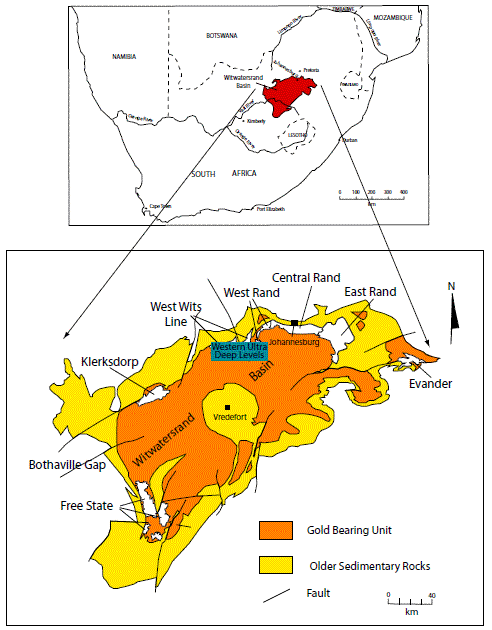
Figure 10J. Location map of the Witwatersrand Basin and its major goldfields. Modified from Robb and Robb (1998).
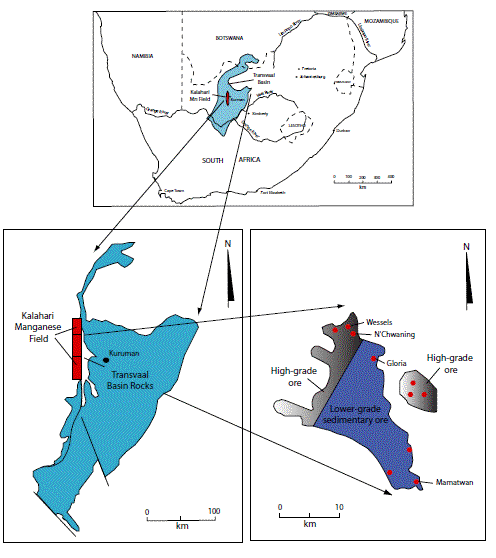
Figure 10K. Location map of the Trasvaal Basin, the Kalahari manganese field, and current producers. Modified from Tiskos and Moore (1998).
USGSのGeology and Nonfuel Mineral Deposits of Africa and the Middle Eastから