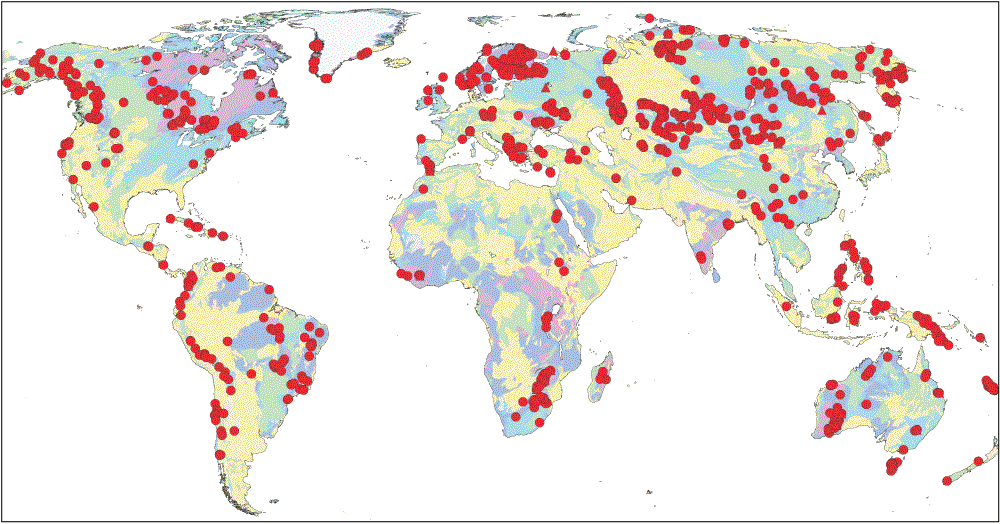
 Figure 1: 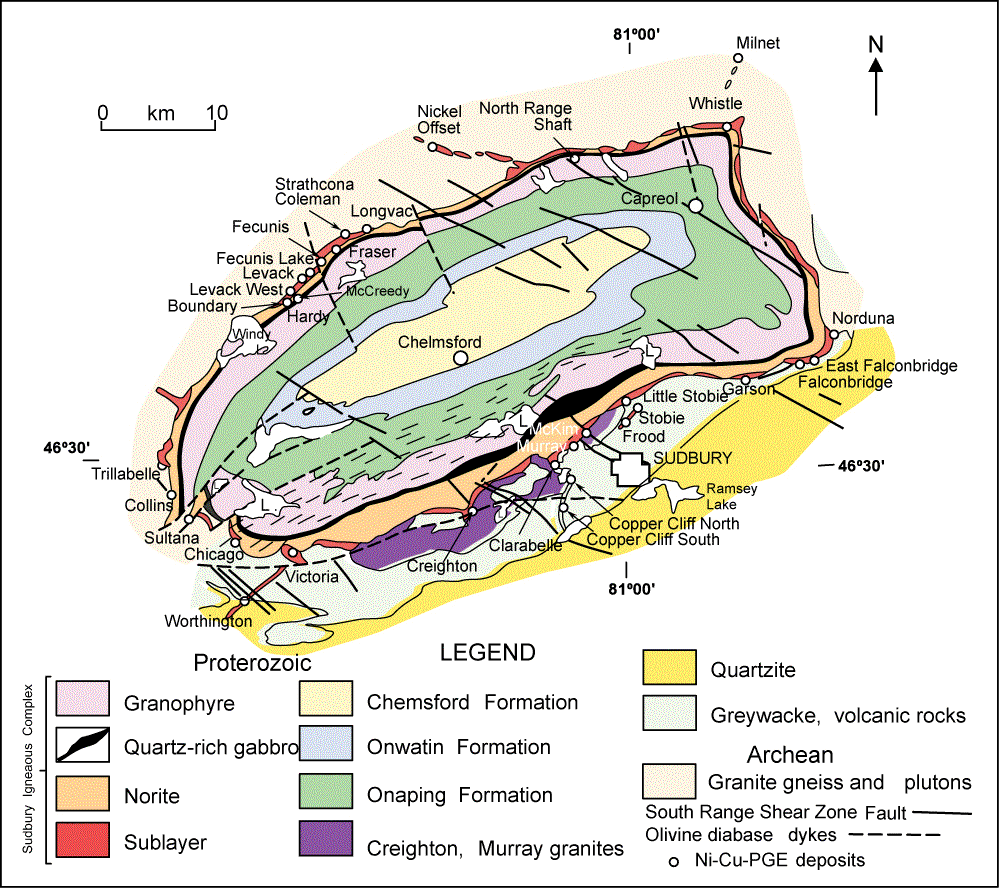 Figure 5: 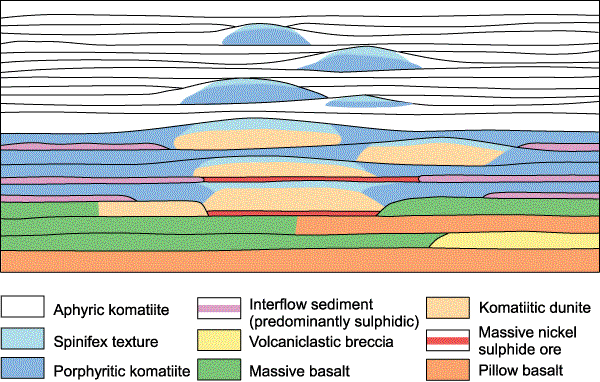
カナダ地質調査所(Geological Survey of Canada)による『Mineral Deposits of Canada Maps of deposits and resources(world)』から |
Magmatic Nickel-Copper-PGE deposits
by O. Roger Eckstrand and Larry J. Hulbert
Contents of this page:
Abstract
Definition
Economic characteristics
Grade and tonnage statistics
Geological attributes
Exploration Models
Knowledge gaps
Acknowledgements
References
Tables
Appendices
Figures
agmatic deposits containing exploitable quantities of nickel, copper, and platinum group elements (PGE) are associated with variable quantities of localized sulphide concentrations in mafi c and ultramafi c rocks. Ni-Cu deposits, nickel being the main economic commodity, are associated with high concentrations of sulphides, and the host bodies are classified based on the nature of the confi ning magmatic environment: (1) meteorite-impact, (2) rift and continental fl ood basalt, (3) komatiitic, and (4) other related mafi c/ultramafi c bodies. Platinum group element deposits are also confined to mafi c/ultramafi c bodies, but are associated with low quantities of sulphides. Reef-type or stratiform PGE deposits form in large, well-layered mafi c/ultramafic intrusions, whereas magmatic breccia-type deposits occurs in stock-like or layered bodies.
The economics and rarity of such deposits with respect to number, grade, tonnage, and mining districts are outlined. In addition, the geological attributes of the various deposit types and subtypes are documented. Exploration models based on district and local scales are discussed, as well as recent advances and knowledge gaps in this field.
 Figure 1:  Figure 5: 
カナダ地質調査所(Geological Survey of Canada)による『Mineral Deposits of Canada Maps of deposits and resources(world)』から |