Hanchen(aの頭に¨)
et al.(2006)による〔『Dissolution kinetics of forsterite olivine at 90-150℃
including effects of the presence of CO2』(4403p)から〕
『CO2の存在の影響を含む90〜150℃でのフォルステライトかんらん石の溶解カイネティックス』
『Abstract
The steady state dissolution rate of San Carlos olivine [Mg1.82Fe0.18SiO4]
in dilute aqueous solutions was measured at 90, 120, and 150℃
and pH ranging from 2 to 12.5. Dissolution experiments were performed
in a stirred flow-through reactor, under either a nitrogen or
carbon dioxide atmosphere at pressures between 15 and 180 bars.
Low pH values were achieved either by adding HCl to the solution
or by pressurising the reactor with CO2,
whereas high pH values were achieved by adding LiOH. Dissolution
was stoichiometric for almost all experiments except for a brief
start-up period. At all three temperatures, the dissolution rate
decreases with increasing pH at acidic to neutral conditions with
a slope of close to 0.5; by regressing all data for 2≦pH≦8.5 and
90℃≦T≦150℃ together, the following correlation for the dissolution
rate in CO2-free solutions is obtained:
r = A aH+n
exp (-Ea/RT )
with A = 0.0854 (+0.67 to -0.0764), the activation energy
Ea = 52.9±6.9 kJ mol-1
K-1, n = 0.46±0.03 (R 2 =
0.98) and r in [mol cm-2 s-1], based
on a 95% confidence interval. Data were fitted to a shrinking
particle model, being based on the assumption of surface controlled
dissolution throughout the whole experiment, with dissolution
extent varying from less than 1% up to complete dissolution, depending
on the experimental conditions. In the presence of CO2
and at low pH, dissolution rates exhibited the same behaviour
as a function of pH, however at pH>5 the rate decreased much more
rapidly with pH than in the presence of N2.
The presence of citric acid, an organic ligand, increased dissolution
rates in respect to the baseline HCl solution significantly.』
1. Introduction
2. Dissolution of olive
2.1. General dissolution kinetics
2.2. Effect of ligands
3. Experimental set-up and methods
4. Modelling and analysis of the experimental measurements
5. Results and discussion
5.1. Experiments without CO2
5.2. Experiments in the presence of CO2
6. Experimental and computational uncertainties
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
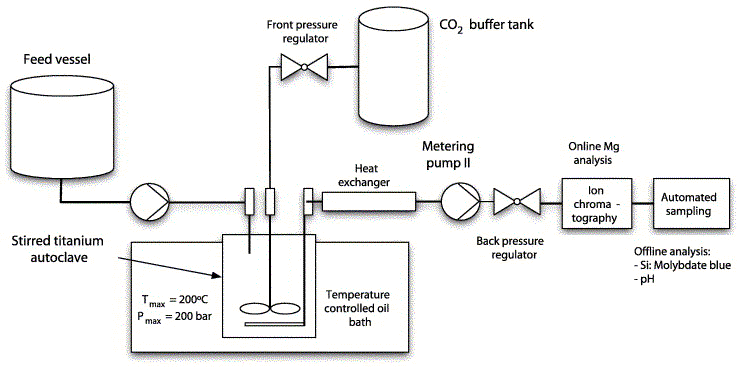
Fig. 1. Scheme of the experimental set-up used for the experiments.
〔Hanchen(aの頭に¨),M., Prigiobbw,V., Storti,G.,
Seward,T.M. and Mazzotti,M.(2006): Dissolution kinetics of
forsterite olivine at 90-150℃ including effects of the presence
of CO2. Geochimica et Cosmochimica
Acta, 70, 4403-4416.から〕 |
戻る
